Introduction
A common use case when you have data in a spreadsheet or database, is to find ways of making that data more visually appealing to others. This is the subject of today's post, where we'll walk through a simple Python script that generates presentation slides based on data in a spreadsheet using both the Google Sheets and Slides APIs.Specifically, we'll take all spreadsheet cells containing values and create an equivalent table on a slide with that data. The Sheet also features a pre-generated pie chart added from the Explore in Google Sheets feature that we'll import into a blank slide. Not only do we do that, but if the data in the Sheet is updated (meaning the chart is as well), then so can the imported chart image in the presentation. These are just two examples of generating slides from spreadsheet data. The example Sheet we're getting the data from for this script looks like this:
The data in this Sheet originates from the Google Sheets API codelab. In the codelab, this data lives in a SQLite relational database, and in the previous post covering how to migrate SQL data to Google Sheets, we "imported" that data into the Sheet we're using. As mentioned before, the pie chart comes from the Explore feature.
Using the Google Sheets & Slides APIs
The scopes needed for this application are the read-only scope for Sheets (to read the cell contents and the pie chart) and the read-write scope for Slides since we're creating a new presentation:'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets.readonly'— Read-only access to Google Sheets and properties'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/presentations'— Read-write access to Slides and Slides presentation properties
SHEETS variable while the one for Slides goes to SLIDES.Start with Sheets
The first thing to do is to grab all the data we need from the Google Sheet using the Sheets API. You can either supply your own Sheet with your own chart, or you can run the script from the earlier post mentioned earlier to create an identical Sheet as above. In either case, you need to provide the Sheet ID to read from, which is saved to thesheetID variable. Using its ID, we call spreadsheets().values().get() to pull out all the cells (as rows & columns) from the Sheet and save it to orders:sheetID = '. . .' # use your own!
orders = SHEETS.spreadsheets().values().get(range='Sheet1',
spreadsheetId=sheetID).execute().get('values')
The next step is to call spreadsheets().get() to get all the sheets in the Sheet —there's only one, so grab it at index 0. Since this sheet only has one chart, we also use index 0 to get that:sheet = SHEETS.spreadsheets().get(spreadsheetId=sheetID,
ranges=['Sheet1']).execute().get('sheets')[0]
chartID = sheet['charts'][0]['chartId']
That's it for Sheets. Everything from here on out takes places in Slides.Create new Slides presentation
A new slide deck can be created withSLIDES.presentations().create()—or alternatively with the Google Drive API which we won't do here. We'll name it, "Generating slides from spreadsheet data DEMO" and save its (new) ID along with the IDs of the title and subtitle textboxes on the (one) title slide created in the new deck:DATA = {'title': 'Generating slides from spreadsheet data DEMO'}
rsp = SLIDES.presentations().create(body=DATA).execute()
deckID = rsp['presentationId']
titleSlide = rsp['slides'][0]
titleID = titleSlide['pageElements'][0]['objectId']
subtitleID = titleSlide['pageElements'][1]['objectId']
Create slides for table & chart
A mere title slide doesn't suffice as we need a place for the cell data as well as the pie chart, so we'll create slides for each. While we're at it, we might as well fill in the text for the presentation title and subtitle. These requests are self-explanatory as you can see below in thereqs variable. The SLIDES.presentations().batchUpdate() method is then used to send the four commands to the API. Upon return, save the IDs for both the cell table slide as well as the blank slide for the chart:reqs = [
{'createSlide': {'slideLayoutReference': {'predefinedLayout': 'TITLE_ONLY'}}},
{'createSlide': {'slideLayoutReference': {'predefinedLayout': 'BLANK'}}},
{'insertText': {'objectId': titleID, 'text': 'Importing Sheets data'}},
{'insertText': {'objectId': subtitleID, 'text': 'via the Google Slides API'}},
]
rsp = SLIDES.presentations().batchUpdate(body={'requests': reqs},
presentationId=deckID).execute().get('replies')
tableSlideID = rsp[0]['createSlide']['objectId']
chartSlideID = rsp[1]['createSlide']['objectId']
Note the order of the requests. The create-slide requests come first followed by the text inserts. Responses that come back from the API are returned in the same order as they were sent, hence why the cell table slide ID comes back first (index 0) followed by the chart slide ID (index 1). The text inserts don't have any meaningful return values and are thus ignored.
Filling out the table slide
Now let's focus on the table slide. There are two things we need to accomplish. In the previous set of requests, we asked the API to create a "title only" slide, meaning there's (only) a textbox for the slide title. The next snippet of code gets all the page elements on that slide so we can get the ID of that textbox, the only thing on that page:rsp = SLIDES.presentations().pages().get(presentationId=deckID,
pageObjectId=tableSlideID).execute().get('pageElements')
textboxID = rsp[0]['objectId']
On this slide, we need to add the cell table for the Sheet data, so a create-table request takes care of that. The required elements in such a call include the ID of the slide the table should go on as well as the total number of rows and columns desired. Fortunately all that are available from tableSlideID and orders saved earlier. Oh, and add a title for this table slide too. Here's the code:reqs = [
{'createTable': {
'elementProperties': {'pageObjectId': tableSlideID},
'rows': len(orders),
'columns': len(orders[0])},
},
{'insertText': {'objectId': textboxID, 'text': 'Toy orders'}},
]
rsp = SLIDES.presentations().batchUpdate(body={'requests': reqs},
presentationId=deckID).execute().get('replies')
tableID = rsp[0]['createTable']['objectId']
Another call to SLIDES.presentations().batchUpdate() and we're done, saving the ID of the newly-created table. Next, we'll fill in each cell of that table.Populate table & add chart image
The first set of requests needed now fill in each cell of the table. The most compact way to issue these requests is with a double-for loop list comprehension. The first loops over the rows while the second loops through each column (of each row). Magically, this creates all the text insert requests needed.reqs = [
{'insertText': {
'objectId': tableID,
'cellLocation': {'rowIndex': i, 'columnIndex': j},
'text': str(data),
}} for i, order in enumerate(orders) for j, data in enumerate(order)]
The final request "imports" the chart from the Sheet onto the blank slide whose ID we saved earlier. Note, while the dimensions below seem completely arbitrary, be assured we're using the same size & transform as a blank rectangle we drew on the slide earlier (and read those values from). The alternative would be to use math to come up with your object dimensions. Here is the code we're talking about, followed by the actual call to the API:
reqs.append({'createSheetsChart': {
'spreadsheetId': sheetID,
'chartId': chartID,
'linkingMode': 'LINKED',
'elementProperties': {
'pageObjectId': chartSlideID,
'size': {
'height': {'magnitude': 7075, 'unit': 'EMU'},
'width': {'magnitude': 11450, 'unit': 'EMU'}
},
'transform': {
'scaleX': 696.6157,
'scaleY': 601.3921,
'translateX': 583875.04,
'translateY': 444327.135,
'unit': 'EMU',
},
},
}})
SLIDES.presentations().batchUpdate(body={'requests': reqs},
presentationId=deckID).execute()
Once all the requests have been created, send them to the Slides API then we're done. (In the actual app, you'll see we've sprinkled various print() calls to let the user knows which steps are being executed.Conclusion
The entire script clocks in at just under 100 lines of code... see below. If you run it, you should get output that looks something like this:$ python3 slides_table_chart.py ** Fetch Sheets data ** Fetch chart info from Sheets ** Create new slide deck ** Create 2 slides & insert slide deck title+subtitle ** Fetch table slide title (textbox) ID ** Create table & insert table slide title ** Fill table cells & create linked chart to Sheets DONEWhen the script has completed, you should have a new presentation with these 3 slides:

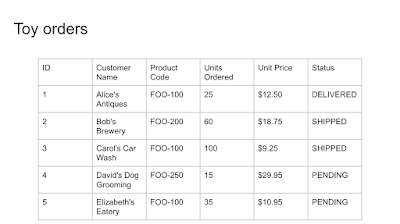
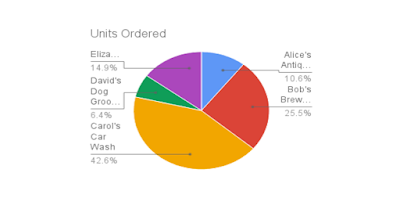
Below is the entire script for your convenience which runs on both Python 2 and Python 3 (unmodified!). If I were to divide the script into major sections, they would be represented by each of the
print() calls above. Here's the complete script—by using, copying, and/or modifying this code or any other piece of source from this blog, you implicitly agree to its Apache2 license:from __future__ import print_function
from apiclient import discovery
from httplib2 import Http
from oauth2client import file, client, tools
SCOPES = (
'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets.readonly',
'https://www.googleapis.com/auth/presentations',
)
store = file.Storage('storage.json')
creds = store.get()
if not creds or creds.invalid:
flow = client.flow_from_clientsecrets('client_secret.json', SCOPES)
creds = tools.run_flow(flow, store)
HTTP = creds.authorize(Http())
SHEETS = discovery.build('sheets', 'v4', http=HTTP)
SLIDES = discovery.build('slides', 'v1', http=HTTP)
print('** Fetch Sheets data')
sheetID = '. . .' # use your own!
orders = SHEETS.spreadsheets().values().get(range='Sheet1',
spreadsheetId=sheetID).execute().get('values')
print('** Fetch chart info from Sheets')
sheet = SHEETS.spreadsheets().get(spreadsheetId=sheetID,
ranges=['Sheet1']).execute().get('sheets')[0]
chartID = sheet['charts'][0]['chartId']
print('** Create new slide deck')
DATA = {'title': 'Generating slides from spreadsheet data DEMO'}
rsp = SLIDES.presentations().create(body=DATA).execute()
deckID = rsp['presentationId']
titleSlide = rsp['slides'][0]
titleID = titleSlide['pageElements'][0]['objectId']
subtitleID = titleSlide['pageElements'][1]['objectId']
print('** Create 2 slides & insert slide deck title+subtitle')
reqs = [
{'createSlide': {'slideLayoutReference': {'predefinedLayout': 'TITLE_ONLY'}}},
{'createSlide': {'slideLayoutReference': {'predefinedLayout': 'BLANK'}}},
{'insertText': {'objectId': titleID, 'text': 'Importing Sheets data'}},
{'insertText': {'objectId': subtitleID, 'text': 'via the Google Slides API'}},
]
rsp = SLIDES.presentations().batchUpdate(body={'requests': reqs},
presentationId=deckID).execute().get('replies')
tableSlideID = rsp[0]['createSlide']['objectId']
chartSlideID = rsp[1]['createSlide']['objectId']
print('** Fetch table slide title (textbox) ID')
rsp = SLIDES.presentations().pages().get(presentationId=deckID,
pageObjectId=tableSlideID).execute().get('pageElements')
textboxID = rsp[0]['objectId']
print('** Create table & insert table slide title')
reqs = [
{'createTable': {
'elementProperties': {'pageObjectId': tableSlideID},
'rows': len(orders),
'columns': len(orders[0])},
},
{'insertText': {'objectId': textboxID, 'text': 'Toy orders'}},
]
rsp = SLIDES.presentations().batchUpdate(body={'requests': reqs},
presentationId=deckID).execute().get('replies')
tableID = rsp[0]['createTable']['objectId']
print('** Fill table cells & create linked chart to Sheets')
reqs = [
{'insertText': {
'objectId': tableID,
'cellLocation': {'rowIndex': i, 'columnIndex': j},
'text': str(data),
}} for i, order in enumerate(orders) for j, data in enumerate(order)]
reqs.append({'createSheetsChart': {
'spreadsheetId': sheetID,
'chartId': chartID,
'linkingMode': 'LINKED',
'elementProperties': {
'pageObjectId': chartSlideID,
'size': {
'height': {'magnitude': 7075, 'unit': 'EMU'},
'width': {'magnitude': 11450, 'unit': 'EMU'}
},
'transform': {
'scaleX': 696.6157,
'scaleY': 601.3921,
'translateX': 583875.04,
'translateY': 444327.135,
'unit': 'EMU',
},
},
}})
SLIDES.presentations().batchUpdate(body={'requests': reqs},
presentationId=deckID).execute()
print('DONE')
As with our other code samples, you can now customize it to learn more about the API, integrate into other apps for your own needs, for a mobile frontend, sysadmin script, or a server-side backend!

